What is RPET material?
RPET stands for Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate. It’s a type of plastic material made from recycled PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles, containers, and other plastic waste. PET is the common plastic used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and textiles, and when it’s recycled, it is transformed into RPET, which can then be used to create new products. One ton of recycled PET gauze equals 67,000 plastic bottles, 4.2 tons of carbon dioxide, 0.0364 tons of oil, and 6.2 tons of water. However, only a portion of it is currently utilized, with the remainder being discarded indiscriminately, resulting in resource waste and environmental pollution.
Key characteristics of RPET:
- Recycled Content: RPET is made by reprocessing used PET materials, making it more environmentally friendly compared to virgin PET, which requires new raw materials.
- Durability: RPET is strong, lightweight, and durable, similar to the original PET plastic.
- Sustainability: By recycling PET, RPET helps reduce waste and the need for virgin materials, contributing to sustainability efforts in packaging, clothing, and other products. One ton of recycled PET gauze equals 67,000 plastic bottles, 4.2 tons of carbon dioxide, 0.0364 tons of oil, and 6.2 tons of water. However, only a portion of it is currently utilized, with the remainder being discarded indiscriminately, resulting in resource waste and environmental pollution.
- Versatility: It can be used for various applications, such as:
- Textiles (e.g., clothing, shoes, and bags)
- Packaging (e.g., bottles, containers)
- Industrial products (e.g., insulation, automotive parts)
What your recycled PET bottles actually become?
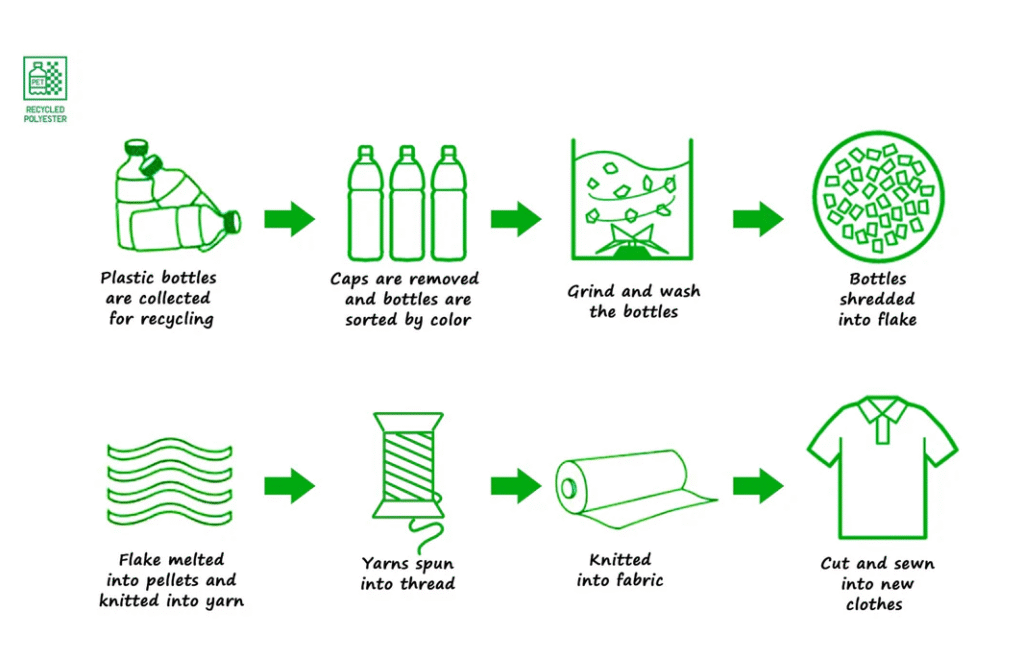
After bottles are collected, cleaned, and shredded into flakes, they become a raw material for several major industries:
- Polyester Staple Fibre (PSF): This is the biggest one. These flakes are melted and spun into fibres for clothes (like fleece jackets), carpets, and the filling in your pillows and duvets. A huge portion of non-cotton textiles comes from this.
- New Packaging (Thermoforming): High-quality, clear flakes are melted into sheets and then moulded into new packaging, like the transparent “clamshell” containers for salads, fruits, and sandwiches.
- Industrial Strapping: The strength of PET makes it perfect for creating those tough plastic straps used to bundle heavy goods for shipping, often replacing steel. Green bottles are frequently used for this.
- Bottle-to-Bottle Recycling: This is the ideal “closed-loop” scenario. The highest-purity flakes go through an intensive cleaning process to become food-grade again, allowing them to be made back into new water or soda bottles.
The key takeaway is that the quality of the recycling process directly determines which of these paths a bottle can take. Cleaner flakes lead to higher-value products.
Differences Between RPET (Recycled Polyester) and Regular Polyester
RPET (recycled polyester) and regular polyester differ significantly in several aspects. Below are the main distinctions:
1. Raw Material Source and Environmental Impact
- RPET: The yarn is made from recycled plastic bottles (e.g., water bottles, soda bottles) through processes like crushing, cleaning, and melting. Producing one ton of RPET yarn saves 6 tons of petroleum resources and reduces carbon emissions, offering notable environmental benefits.
- Regular Polyester: It is synthesized directly from petroleum-derived chemicals (PTA and MEG), relying on non-renewable resources. Its production involves higher carbon emissions and is less environmentally friendly.
2. Physical Properties
- Strength and Elasticity:
- Regular polyester has slightly higher strength (short fiber strength: 2.6–8.0 cN/dtex) and better impact resistance than RPET (4 times that of nylon and 20 times that of viscose fiber).
- Both have elasticity comparable to wool, with 5%–6% elongation recovery, excellent wrinkle resistance, and dimensional stability.
- Abrasion Resistance: Regular polyester ranks second only to nylon in abrasion resistance, while RPET is slightly inferior but still outperforms natural fibers.
- Tensile Strength Difference: Due to purity limitations in recycled materials, RPET’s fiber strength is typically 10%–30% lower than regular polyester.
3. Heat and Chemical Resistance
- Heat Resistance: Both are thermoplastic fibers with a high melting point (~260°C), exhibiting the best heat resistance and insulation among synthetic fibers.
- Melting Resistance: Both perform poorly in this regard, easily forming holes when exposed to sparks.
- Chemical Resistance: Both resist acids, alkalis, oxidants, and UV rays, but RPET may have slightly lower tolerance to strong chemicals due to the recycling process.
4. Applications and Market
- RPET: Focused on sustainability, it is widely used in fashion (e.g., T-shirts, dresses), home textiles (e.g., curtains, cushions), and bags, with strong demand in European and American markets driven by policies.
- Regular Polyester: Dominates mainstream markets like apparel and industrial fabrics due to its low cost and stable performance, though it faces restrictions from environmental regulations.
5. Other Characteristics
- Dyeability: Both are difficult to dye due to their molecular structure but exhibit good color fastness.
- Moisture Absorption: Both have poor moisture absorption (~0.4%), leading to static electricity, but they dry quickly after washing and resist deformation.
RPET’s core advantage lies in resource recycling and carbon reduction, making it ideal for eco-friendly products. Regular polyester excels in performance stability and cost-effectiveness. With technological advancements, RPET’s performance gap is narrowing, and its applications are expected to expand further in the future.
More and more big brands are using more and more RPET materials:
Samsonite
Samsonite’s “sustainable materials” strategy includes using rPET (and other recycled materials) to make some soft luggage, backpacks, linings, webbing, etc., and many of its collections contain rPET.
American Tourister
Its Urban Track duffle bag line, launched in 2022, claims to be “made entirely from recycled materials,” including rPET.
TUMI
In the design of some of its products (such as the classic Alpha/Bravo series), rPET is used in components such as linings, webbing, and zipper tapes to reduce reliance on new plastics.
Troika
The brand explicitly uses “rPET / Blue-Cycle (including ocean plastic recycling)” as its material source, and has launched a variety of rPET backpacks and accessories.
Nike
Nike began using RPET fabric as early as 2010, launching several eco-friendly athletic shoes and apparel.
For example, their “Space Hippie” series is made from recycled plastic bottles and other waste materials, making it not only environmentally friendly but also futuristic.
Burberry
In 2020, Burberry announced that it would phase out traditional plastic packaging and switch to RPET material.
At the same time, some of their trench coats and accessories also began using RPET fabric, maintaining their British style while reflecting their environmental commitment.
Gucci
Gucci’s “Off The Grid” collection
emphasizes sustainable fashion, making extensive use of RPET fabric.
The bags, shoes, and clothing in this collection are not only highly designed but also imbued with an eco-friendly spirit.
Typical applications of RPET in bags
Due to its wear resistance, lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and wide range of available colors, RPET has become a popular material for many everyday bags such as backpacks, shoulder bags, tote bags, and portfolio bags.
1. Soft-Shell Suitcases
- Materials: 600D / 900D / 1200D RPET Oxford cloth, reinforced with polyester layers and protective coatings to enhance overall strength.
- Features: Lighter weight and more environmentally friendly.
- Applications: Ideal for international luggage brands developing new sustainable product lines.
2. Outdoor Backpacks
- Materials: RPET Oxford paired with a water-repellent coating; optional recycled TPU or silicone waterproof layers.
- Features: Durable, weather-resistant, and eco-friendly.
- Applications: Suitable for light outdoor activities such as urban camping, day hiking, and commuting adventures.
3. Business Laptop Bags & Accessory Cases
- Materials: RPET fibers combined with foam padding; RPET lining is commonly used for interiors.
- Applications: Widely adopted by technology brands, consumer electronics companies, and e-commerce private-label brands.
4. RPET PU Synthetic Leather
- Structure: RPET fibers serve as the base fabric, coated with environmentally friendly PU.
- Features:
- Can replace conventional PU materials
- Suitable for handbags, wallets, and card holders
- Offers a look and feel similar to genuine leather
- Significantly lower carbon footprint
- Market Trend: Highly popular among European fashion and lifestyle brands as sustainable materials gain traction.






